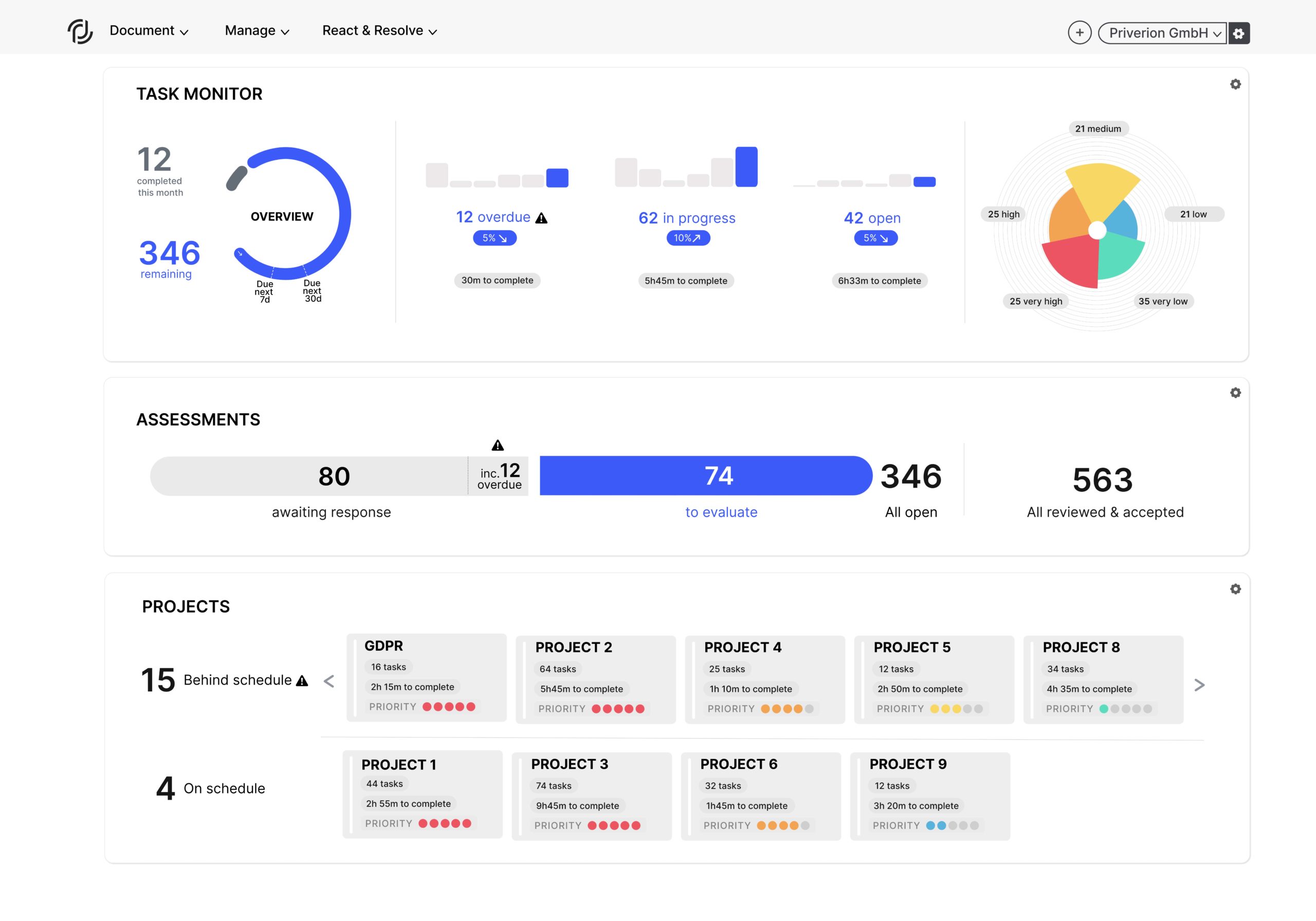
Our privacy modules allow to maintain all the necessary elements of privacy compliance.
Learn moreDocument
Record of Processing Activities (ROPA)
Data Protection Impact Assessments
Reports & Downloads
Legitimate Interests Documentation
Retention & Deletion Periods
Automated Decision Making and AI
Technical and Organizational Measures (TOM)
Assessments
Vendors
Policies
Data Collection Points
Privacy Center
Meetings & Activities
Manage
Projects
Vendor Risk
Process Risk
Privacy Audit
React & Resolve
Task Management
Projects
Incident Management
Data Subject Requests